Geological Setting Of Sarawak
The area is also situated along the structural feature dividing.
Geological setting of sarawak. The book is a comprehensive compilation of all aspects of the geology of Northwest Borneo Sarawak Brunei and Sabah and the contiguous South China and Sulu Seas. In Sabah the Western Cordillera. The Miri zone consists of sedimentary rocks deposited under shallow marine estuarine and fluvial systems during Neogene.
Originally the latter probably connected with high level caves above Batu Nigel. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 76 312-333. Regional geological cross-section through Brunei and Sarawak.
Brunei Darussalam has a convoluted boundary with Sarawak and its geology has much in common with western Sabah and eastern Sarawak. The section is based on offshore seismic reflection data Sandal 1996 onshore geological maps Wilford 1960 and models for the tectonic development of northern Borneo from James 1984 and Hutchison 1996ab and our own geological fieldwork in Brunei. 32 Full PDFs related to this paper.
The petroleum geology and resources of Malaysia 1 273-290. On the basis of tectonostratigraphic zonation the entire Sarawak Basin is segmented into seven 7 geological provinces namely the West Baram Balingian Central Luconia Tinjar Tatau West and SW Luconia and SW Sarawak provinces Fig. Stratigraphic charts illustrate their relationships across the whole region.
The study area Tubau located in Central Sarawak is underlain by many interesting geological structures. Petroleum Geology and Resources of Malaysia 1999. There are also several occurrences of economic deposits such as coal and limestone.
The geology in Sarawak deepwater is closely associated and linked to the tectonic development of the South China Sea Basin. Geological setting of Sarawak. A short summary of this paper.
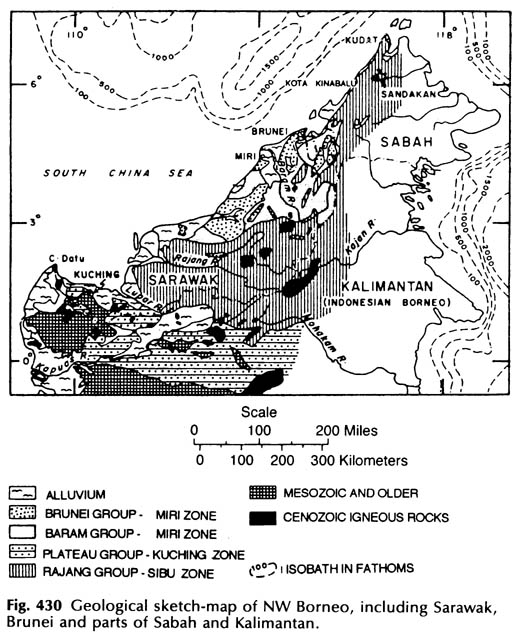
The Luconia Block constitutes the northern segment of the Sarawak Basin Fig. Sarawak Chamber is developed in the thinly-bedded basal limestones. The regional geology of the Sarawak state is divided into three major zones namely Kuching Sibu and Miri.
TECTONIC AND GEOLOGICAL SETTING Central Sarawak occupying the northwestern part of Borneo lies at the intersection ofthree major plates the Eurasian Indo-Australian and Philippines located to the north south and east respectively Fig. Geological setting of Sarawak. Geologic setting The Baram Delta is one of seven geological provinces found offshore the Sarawak fo reland Basin 17 -18 and is the most prolific of all the g eological provinces in the basin 10.
M Madon CL Kim R Wong. In Sarawak the mountains are constructed of Upper Cretaceous to Lower Eocene greenschist facies shaly turbiditic Rajang Group uplifted before the end of the Eocene. Correlation tables descriptions and ages of all major sedimentary formations of Sarawak Brunei and Sabah Petrology geochemistry and ages of all volcanic and plutonic formations of North West Borneo and their tectonic significance Economic geology including the geological setting.
The structure and stratigraphy of deepwater Sarawak Malaysia. Geological setting of Sarawak. Download Full PDF Package.
The main objective of this study was to determine the. Structurally SW Sarawak basin is a southward sloping basement characterized by passive margin tectonic that has undergone through varioius tectonic phases viz Triassic extension Cretaceous transpression and Oligo-Miocene compression. The major Neogene sedimentary formations are a Sibuti b Lambir c Tukau and d Miri Fig.
Several prominent workers from research institutions and from oil exploration companies have provided critical insight on the evolution of the Late Mesozoic to Tertiary aged South China Sea Basin. Coals of Sarawak WAN HAsIAH ABDULLAH Department of Geology University of Malaya 50603 Kuala Lumpur An organic petrological study was performed on Tertiary coals from the Merit-Pila and the Mukah-Balingian coalfields of Sarawak. The Balingian Province is part of peripheral foreland basin fill of Sarawak Basin which formed due to the closure of the Rajang Sea and the Sarawak Orogeny during the Late Eocene Figure 2.
It lies almost at the base of the limestone and as the Paku lowered its base level the water moved eastwards down dip aided by the local east-west joints to form the Nasib Bagus system.